

Liposuction doesn’t remove cellulite. Cellulite is a common skin condition that causes your skin to look dimpled and often appears on your abdomen, buttocks, hips, and thighs. Liposuction only removes soft tissue from your body. Since cellulite is caused by fibrous bands of tissue under the skin rather than soft, fatty tissue, liposuction doesn’t affect it.
Liposuction and a tummy tuck (abdominoplasty) are both cosmetic procedures, but they serve different purposes:
The amount of weight you lose varies based on your goals and the amount of fat removed. On average, liposuction results in fat loss but is not a solution for significant weight loss or overall body weight reduction.
Several minimally invasive or noninvasive liposuction alternatives are available, which can speed up recovery and reduce scarring. These include:

360 liposuction, or Lipo360™, removes fat from several areas of the body at once, focusing on the midsection, including the upper and lower abdomen, love handles, and sometimes the back. Unlike traditional liposuction, which targets a single area, Lipo360 provides a more comprehensive fat removal in a single procedure.
Liposuction is a permanent solution for stubborn fat deposits. If diet and exercise haven’t worked for you, consider discussing liposuction with your healthcare provider. While it can improve body contour, it's not a weight loss treatment, and maintaining a healthy weight post-procedure is crucial to keeping your new shape.
Botox has been used for decades in the medical industry. It may be recommended for treating:
Yes, Botox can help reduce pain by blocking nerve signals that control muscle activity, leading to relaxation and pain relief. Botox injections can treat:
Botox is made from a bacterium called Clostridium botulinum. The specific neurotoxin used for medical injections is type A, which is produced in a lab for safety and efficacy.
Technicians dilute and sterilize the toxin to prevent botulism, a serious nervous system disorder caused by large amounts of botulinum toxins.
Botox is generally safe when administered by a licensed healthcare provider. Always consult your medical team to ensure Botox injections are right for you.
Before treatment, inform your healthcare provider about any medications or supplements you are taking. Avoid alcohol and blood thinners like NSAIDs and Warfarin® 24 hours before the procedure to reduce the risk of bruising.
Botox is an outpatient procedure. A fine needle injects small amounts of Botox into the treatment area. Your healthcare provider may give you anesthesia if you are receiving injections for certain conditions, such as an overactive bladder.
After treatment, you can return to most activities right away. To minimize side effects like swelling or bruising, follow these tips:
Common side effects include:
People who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have neuromuscular diseases should avoid Botox.
Most people notice the effects of Botox around the third or fourth day after treatment, with full results visible within 10 to 14 days.
Botox results usually last between three to six months, after which the muscles regain movement and wrinkles return. To maintain results, you can receive more Botox injections as advised by your healthcare provider.
Botox is generally safe, but you should contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience any of the following:

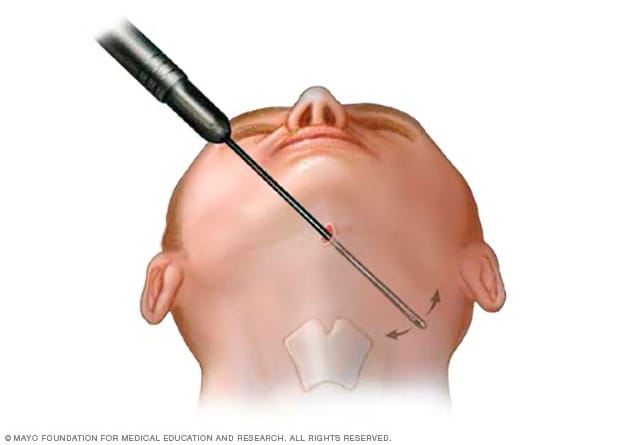
Botox is FDA-approved for treating chronic migraines. It works by blocking pain signals at nerve endings. Best results are usually seen after the second or third treatment session.
The needles used for Botox injections are small, so most people feel little to no discomfort. If you’re concerned, your healthcare provider can apply a numbing gel to the area.
While Botox isn’t likely to harm your baby, most healthcare providers recommend waiting until after pregnancy or breastfeeding to undergo treatment for safety reasons.
Yes, besides Botox, options include:
Dysport may offer quicker results, but Botox tends to last longer. Discuss with your healthcare provider to decide which is best for you.
Yes, it is safe. There are no known adverse interactions between Botox and the COVID-19 vaccine, though there have been rare cases of temporary swelling in people with dermal fillers.
