

Liposuction, also known as lipoplasty, is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of excess fat from specific areas of the body. The procedure is typically used to contour the abdomen, hips, thighs, buttocks, and other areas where diet and exercise alone have not been successful. Liposuction is a popular cosmetic surgery procedure that can help people achieve a slimmer and more proportional body shape.
Liposuction techniques may be used to reduce localized fat deposits of the:
Liposuction can be performed alone or in conjunction with other plastic surgery procedures, such as a facelift, breast reduction, or a tummy tuck.
Liposuction is not a treatment for obesity or a substitute for proper diet and exercise. It works best for people of normal weight who have some extra fat. For optimal results, the skin should be firm and elastic. Skin that is soft and thin from stretch marks, weight loss, or natural aging may not reshape as well and may require additional surgeries to remove and tighten excess skin. Liposuction is also not an effective treatment for cellulite.
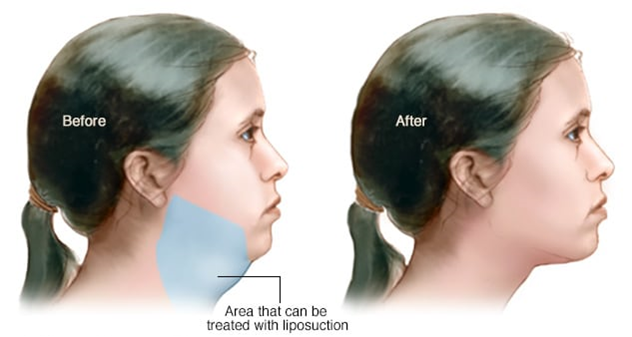
Blue shading shows the area under the chin that can be treated with liposuction.
Liposuction is a type of surgery that uses suction to remove fat from specific areas of the body, such as the stomach, hips, thighs, buttocks, arms, or neck. It shapes these areas through a process called contouring. Other names for liposuction include lipoplasty and body contouring.
Liposuction is not considered an overall weight-loss method or a weight-loss alternative. People who are overweight can typically lose more weight through diet and exercise or through other kinds of surgery. Liposuction may be suitable if you have a lot of body fat in specific places but otherwise have a stable body weight.
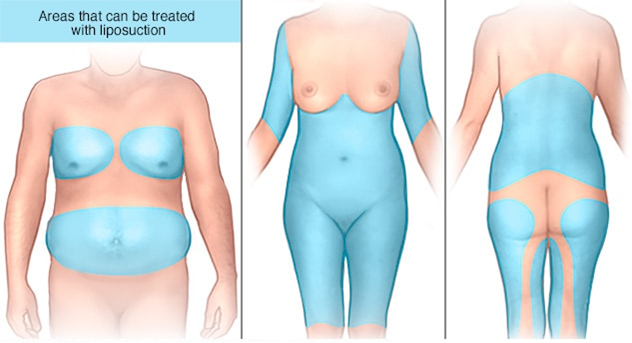
Blue shading shows areas on the body — including the abdomen, chest, back, legs, and arms — that can be treated with liposuction.
Liposuction removes fat from areas of the body that don't respond to diet and exercise. These include:
In addition, liposuction can sometimes be used to reduce extra breast tissue in men — a condition called gynecomastia.
When you gain weight, fat cells get bigger. Liposuction lowers the number of fat cells in a specific area. The amount of fat removed depends on what the area looks like and the volume of fat. The resulting shape changes are usually permanent as long as your weight remains the same.
After liposuction, the skin molds itself to the new shapes of the treated areas. If you have good skin tone and elasticity, the skin usually looks smooth. If your skin is thin and not elastic, the skin in the treated areas may look loose.
Liposuction doesn't help with dimpled skin from cellulite or other differences in the surface of the skin. Liposuction also doesn't remove stretch marks.
To have liposuction, you must be in good health without conditions that could make surgery more difficult. These can include blood flow problems, coronary artery disease, diabetes, or a weak immune system.
As with any surgery, liposuction has risks. These risks include bleeding and a reaction to anesthesia. Other risks specific to liposuction include:
The risk of complications rises if the surgeon works on larger body surfaces or does multiple procedures during the same operation. Talk to the surgeon about how these risks apply to you.
Before the procedure, discuss with your surgeon what to expect from the surgery. Your surgeon will review your medical history and ask about any medical conditions you may have. Tell the surgeon about any medicines, supplements, or herbs you are taking.
Your surgeon will recommend that you stop taking certain medicines, such as blood thinners or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), at least a week before surgery. You also may need to get certain lab tests before your procedure.
If only a small amount of fat is to be removed, the surgery may be done in a clinic or medical office. If a large amount of fat will be removed or if you have other procedures done at the same time, the surgery may take place in a hospital. In either case, find someone to drive you home and stay with you for at least the first night after the procedure.
During suction-assisted liposuction, the most common type of liposuction, the surgeon uses a thin tube attached to a vacuum to remove fat from under the skin. In some cases, the surgeon might insert the tube through several points to treat an area from different angles.
Before your liposuction procedure, the surgeon may mark circles and lines on the areas of your body to be treated. Photos also may be taken so that before and after images can be compared.
How your liposuction procedure is done depends on the specific technique that's used. Your surgeon will select the technique based on your treatment goals, the area of your body to be treated, and whether you have had other liposuction procedures in the past.
Some liposuction procedures use local or regional anesthetics to numb a specific area of the body. You may also be given a medicine, usually through an IV, to help you stay calm and relaxed. Other procedures may use general anesthetics to put you in a sleep-like state.
The surgical team monitors your heart rate, blood pressure, and blood oxygen level during the procedure. If you feel pain during the procedure, inform your surgeon so the medicine or procedure can be adjusted.
The procedure may last up to several hours, depending on how much fat is being removed. If you've had general anesthesia, you'll wake up in a recovery room and may spend several hours in the hospital or clinic. If a lot of fluid was removed, you might stay overnight to ensure you are not dehydrated or in shock from fluid loss.
Expect some pain, swelling, and bruising after the procedure. Your surgeon may provide medicines to control the pain and reduce the risk of infection. You may have incisions left open or temporary drains placed to help fluid drain out of your body.
Most people need to wear tight compression garments for a few weeks to help reduce swelling. You may need to wait a few days before returning to work and a few weeks before resuming your usual activities, including exercise.
During recovery, expect some differences in shape as the remaining fat settles into position. It will take weeks to months to see the final results.
Swelling typically goes away within a few weeks, with the treated area looking less bulky. Within several months, expect the treated area to look slimmer. Liposuction results usually last a long time if you maintain your weight. Gaining weight after liposuction can change fat levels in different areas of the body.
Liposuction is a cosmetic fat removal procedure that permanently removes fat cells (adipocytes) from specific areas of your body, such as the abdomen, to improve body contours. It helps get rid of fat deposits that don't respond to diet and exercise. Other names for liposuction are lipoplasty or “lipo.”
You can have a liposuction procedure anywhere on your body where you have deposits of fat. Common areas include:
Candidates for liposuction should meet certain requirements to ensure the procedure is effective and safe. Suitable candidates include:
You might not be a candidate if you:
Age is generally not a factor, but people over 65 may have skin with less firmness or elasticity.
Yes, people of any sex can undergo liposuction. For men or people assigned male at birth, it may help treat gynecomastia or enlarged male breast tissue.
You might consider liposuction if you:
Liposuction is not a weight-loss solution and does not treat obesity. It’s used to remove unwanted fat from specific areas, not as a full-body weight-loss method. If you have excess weight, consult your healthcare provider about weight management options.
Liposuction is one of the most common plastic surgery procedures. In the U.S., over 200,000 procedures occur each year, representing 15% to 20% of all plastic surgeries worldwide.
Different types of liposuction include:
A plastic surgeon performs liposuction. Look for a board-certified surgeon with specialized training and experience, ideally affiliated with a major medical center.
Consider these questions when consulting a plastic surgeon:
Before the procedure, you’ll consult with your surgeon to discuss:
Having realistic expectations and goals is essential. Liposuction treats specific body areas but does not prevent weight gain or cure obesity.
Your surgeon will give you specific instructions to follow before your liposuction surgery. You may need to:
Before your liposuction procedure, your healthcare provider will give you anesthesia, which may be local or general. Once the anesthesia takes effect, your surgeon will:
The procedure may take place in an outpatient setting or a hospital, depending on the amount of fat removed. You will need someone to drive you home afterward.
You may combine liposuction with other cosmetic procedures, such as:
Combining procedures can reduce overall recovery time but may increase risks.
After your procedure, your healthcare provider will discuss:
Common signs of healing include bruising, swelling, and soreness. Compression garments may help reduce swelling and pain. You might also need a temporary drain in the incision.
You won’t feel pain during the procedure due to anesthesia, but you may experience tenderness or soreness afterward. Your provider may prescribe medication or compression garments to manage discomfort.
Benefits include:
Possible risks include:
Recovery time varies based on the amount of fat removed. On average, complete healing takes up to six months. You may need to reduce activities for the first six weeks.
After an outpatient procedure, you might return to work in a few days and feel like yourself within two weeks. Full physical activities may resume after about six weeks.
Scarring is expected, but most people have very small scars. Your provider will give advice on scar care to minimize visibility.
Liposuction is a permanent procedure that removes fat cells from specific areas. However, weight gain is still possible, and liposuction is not a solution for obesity.
You’ll start to see results as swelling decreases, which can take three to six months for full resolution.
Most people don’t need a second procedure unless they want further cosmetic changes. Liposuction is permanent, but weight gain can still occur.
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience:
Liposuction doesn’t remove cellulite. Cellulite is a common skin condition that causes your skin to look dimpled and often appears on your abdomen, buttocks, hips, and thighs. Liposuction only removes soft tissue from your body. Since cellulite is caused by fibrous bands of tissue under the skin rather than soft, fatty tissue, liposuction doesn’t affect it.
Liposuction and a tummy tuck (abdominoplasty) are both cosmetic procedures, but they serve different purposes:
The amount of weight you lose varies based on your goals and the amount of fat removed. On average, liposuction results in fat loss but is not a solution for significant weight loss or overall body weight reduction.
Several minimally invasive or noninvasive liposuction alternatives are available, which can speed up recovery and reduce scarring. These include:
360 liposuction, or Lipo360™, removes fat from several areas of the body at once, focusing on the midsection, including the upper and lower abdomen, love handles, and sometimes the back. Unlike traditional liposuction, which targets a single area, Lipo360 provides a more comprehensive fat removal in a single procedure.
Liposuction is a permanent solution for stubborn fat deposits. If diet and exercise haven’t worked for you, consider discussing liposuction with your healthcare provider. While it can improve body contour, it's not a weight loss treatment, and maintaining a healthy weight post-procedure is crucial to keeping your new shape.
